CBT refers to Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. CBT is a form of psychological treatment that has been demonstrated to be effective for a range of problems including depression, anxiety disorders, alcohol and drug use problems, marital problems, eating disorders and severe mental illness. Numerous research studies suggest that CBT leads to significant improvement in functioning and quality of life. In many studies, CBT has been demonstrated to be as effective as, or more effective than, other forms of psychological therapy or psychiatric medications.
How CBT Can Help?
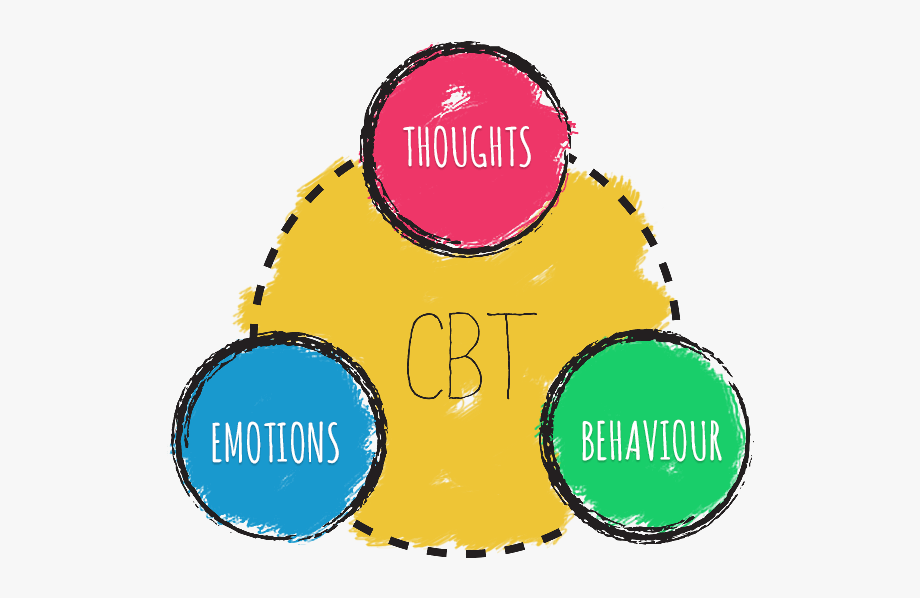
CBT is based on the model that our feelings and actions are influenced by our thinking style, not external factors. Thus the treatment provided emphasizes the cognitive (cognitive) system in an effort to change behavior and emotional state. CBT focuses on replacing negative forms of thinking and behavior with forms of poetic thinking and behavior
Behavior therapy is also known as behavioral modification, training individuals to replace unwanted behavior with healthy behaviors. Unlike psychodynamic therapy, behavioral therapy does not emphasize the subconscious motivations that may exist behind wrong behavior. Behavioral therapists do not identify why their clients behave wrongly instead train them to change their behavior.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy combines a cognitive therapy restructuring approach with behavioral therapy modification techniques. Therapists with their clients identify stressful thoughts and behaviors and change the way they aim to adjust their behavior. Sometimes clients have a central point of their thinking which is a scheme that requires modification. For example, clients with depression may avoid social contact with others and may experience emotional stress caused by their isolation. When asked ‘why?’, The client explained that he was afraid of rejection or what others would do or tell him. Through exploration, clients are able to realize that fear is not a rejection but a belief that it is hopeless, unattractive and unloved. The client will then test the reality of his claim by presenting some of the names of friends and family members who love him and have fun with him. By exposing her to the value of others to her, she can expose irrational thoughts and introduce to her a new way of thinking to change old forms of behavior. This method allows clients to learn to think ‘I am also attractive and loved, therefore I have no difficulty in making new friends in social relations. If sufficient changes are made to the ‘irrational cognition’, the client will experience an important experience of relief from depression.
CBT sessions
If CBT is recommended, you will usually have a session with a therapist once a week or once every two weeks.
Some problems may require more intensive intervention and a therapist may spend several hours at your home to encourage you to face your fears.
Overall, the number of sessions you need will depend on your individual problems and objectives. Treatment usually lasts six weeks to six months
Types of Cognitive Behavior Therapy
According to the British Association of Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapies, “Cognitive and behavioral psychotherapies are a range of therapies based on concepts and principles derived from psychological models of human emotion and behavior. They include a wide range of treatment approaches for emotional disorders, along with a continuum from structured individual psychotherapy to self-help material.”
There are a number of specific types of therapeutic approaches that involve CBT that is regularly used by mental health professionals. Examples of these include:
- Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT): This type of CBT is centered on identifying and altering irrational beliefs. The process of REBT involves identifying the underlying irrational beliefs, actively challenging these beliefs, and finally learning to recognize and change these thought patterns.
- Cognitive Therapy: This form of therapy is centered on identifying and changing inaccurate or distorted thinking patterns, emotional responses, and behaviors.3
- Multimodal Therapy: This form of CBT suggests that psychological issues must be treated by addressing seven different but interconnected modalities, which are behavior, affect, sensation, imagery, cognition, interpersonal factors and drug/biological considerations.4
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy: This type of cognitive-behavioral therapy addresses thinking patterns and behaviors and incorporates strategies such as emotional regulation and mindfulness.
While each type of cognitive-behavioral therapy offers its own unique approach, each centers on addressing the underlying thought patterns that contribute to psychological distress.
Pro and Cons CBT

There are a number of advantages and disadvantages associated with CBT.
Research has shown that CBT can be as effective as medicine in treating depression and other mental health problems. Compared with other talking therapies, CBT can also be completed over a relatively short period of time.
Also, due to the structured nature of CBT, it may not be suitable for people with more complex mental health needs or learning difficulties.
Advantages of CBT
- Research has shown CBT can be as effective as medicine in treating many types of depression and other mental health disorders.
- CBT can be completed in a relatively short period of time compared with other types of talking therapies.
- The highly structured nature of CBT means it can be provided in different formats, including in groups, self-help books, and computer programs.
- Skills you learn in CBT are useful, practical and helpful strategies that can be incorporated into everyday life to help you cope better with future stresses and difficulties.
However, to benefit from CBT, you need to commit yourself to the process. A therapist can help and advise you, but they cannot make your problems go away without your full co-operation.
Disadvantages
- To benefit from CBT, you need to commit yourself to the process. A therapist can help and advise you, but cannot make your problems go away without your co-operation.
- Due to the structured nature of CBT, it may not be suitable for people with more complex mental health needs or learning difficulties.
- Some critics argue that because CBT only addresses current problems and focuses on specific issues, it does not address the possible underlying causes of mental health conditions, such as an unhappy childhood.
- CBT focuses on the individual’s capacity to change themselves (their thoughts, feelings and behaviours), and does not address wider problems in systems or families that often have a significant impact on an individual’s health and wellbeing
It is important to note that CBT does not just involve identifying these thought patterns; it is focused on using a wide range of strategies to help clients overcome these thoughts. Such strategies may include journaling, role-playing, relaxation techniques, and mental distractions.